Archives
- 2026-01
- 2025-12
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2025-09
- 2025-04
- 2025-03
- 2025-02
- 2025-01
- 2024-12
- 2024-11
- 2024-10
- 2024-09
- 2024-08
- 2024-07
- 2024-06
- 2024-05
- 2024-04
- 2024-03
- 2024-02
- 2024-01
- 2023-12
- 2023-11
- 2023-10
- 2023-09
- 2023-08
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2019-07
- 2019-06
- 2019-05
- 2019-04
- 2018-07
-
Pulmonary fibroblasts can regulate the wound healing process
2020-06-29
Pulmonary fibroblasts can regulate the wound healing process by secreting and processing extracellular matrix (ECM), chemokines, and cytokines. However, persistent and atypical fibroblast proliferation can result in ECM accumulation and may trigger the onset or development of pulmonary fibrosis [[17
-
phenethyl In conclusion DDR ECD was shown to be sufficient f
2020-06-29
In conclusion, DDR1 ECD was shown to be sufficient for collagen mediated DDR1 oligomerization, and the oligomerized form binds to collagen with increased affinity. In full length receptors expressed on live cells, DDR1 oligomerization occurred on the cell surface in agreement with the role of DDR1 E
-
These cytokines except for TGF can also
2020-06-29
These cytokines, except for TGF-β can also increase CysLT1R mRNA expression. We further demonstrated that TGF-β and IL-13 were able to increase the proliferation of human BSMC in response to LTD4. BSMC proliferation was CysLT1R-dependent, given that Montelukast ablated this effect. Taken together, o
-
br Disclosure and conflicts of interest br Acknowledgements
2020-06-29
Disclosure and conflicts of interest Acknowledgements This research was supported by grant (BT/PR/11293/BRB/10/849/2008) from Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Government of India and a DST YOS Chair Professorship to PB. The mass spectrometry facility is supported by an institutional program
-
ERR is constitutively active in the absence of endogenous
2020-06-29
ERRγ is constitutively active in the absence of endogenous ligand. However, several synthetic ligands that can repress or induce ERRγ function by disrupting ERRγ-coactivator interactions have been reported to date. The estrogen receptor modulators diethylstilbestrol (DES) and 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4-O
-
br Diverse functions of ERK pathway Same as the
2020-06-29
Diverse functions of ERK pathway Same as the other MAPK cascades, the ERK pathway is activated by several extracellular stimuli and different internal routes. ERK vitally tunes the function of various substrates in all cellular components; the nucleus, cytoplasm, membranes and the cytoskeleton. E
-
Additionally in the presented study both
2020-06-29

Additionally, in the presented study both the NSE values and MFI levels of the CD45−CD34 + CXCR7+ ACY1215 sale correlated positively with the inflammatory parameter – CRP. CXCR7 expression has been found to be enhanced during pathological processes such as inflammation and neoplasms (Janssens et al
-
The in vitro enantioselective metabolism of pesticides has b
2020-06-29
The in vitro enantioselective metabolism of pesticides has been investigated by employing human liver microsomes, which are a reliable resource to perform MCL enantioselective risk assessment in humans (Carrão et al., 2019; de Albuquerque et al., 2018, 2016; Yao et al., 2016). The enantioselective
-
dofetilide Increasing evidence supports that the B cell
2020-06-29
Increasing evidence supports that the B-cell lymphoid malignancies develop from various stages of B-cells, hijacking the mechanisms that drive B-cell differentiation and activation [27]. For instance, mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) originate from the pre-germinal c
-
HBX 41108 Likewise the conserved cysteine in the E protein i
2020-06-29
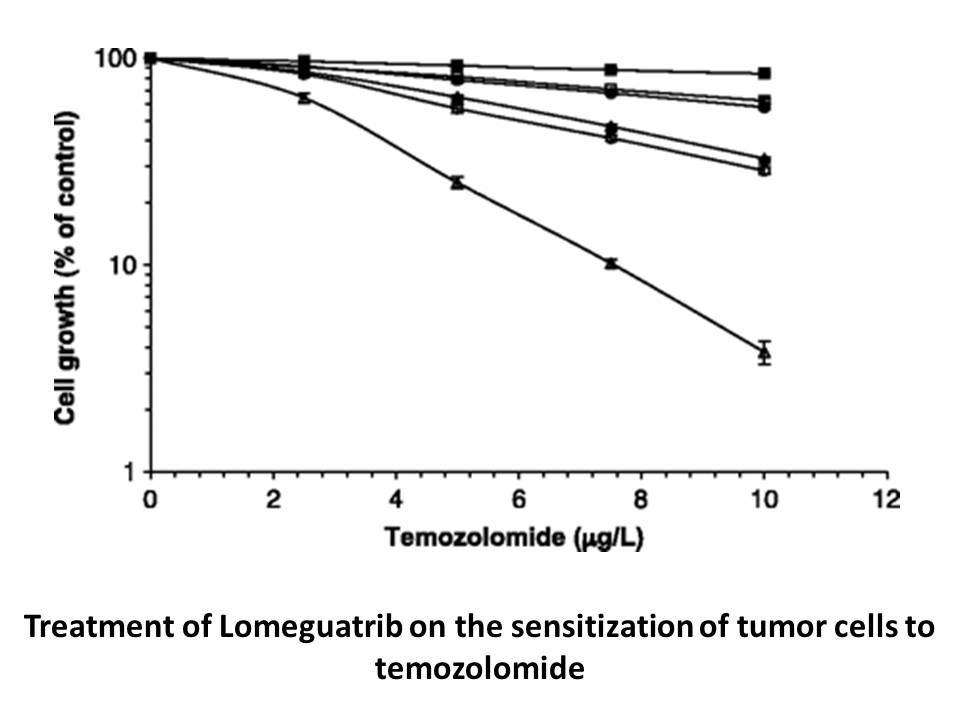
Likewise, the conserved cysteine in the E2 protein is the only residue shown to be essential for the transfer of Ub/Ubl from E2 to the HECT ligases (Dye and Schulman, 2007, Wu et al., 2003). However, all other terminal Ub/Ubl transfer reactions involving E2 enzymes suggest a critical role for the ta
-
The Wnt signaling pathway has been demonstrated to be
2020-06-29
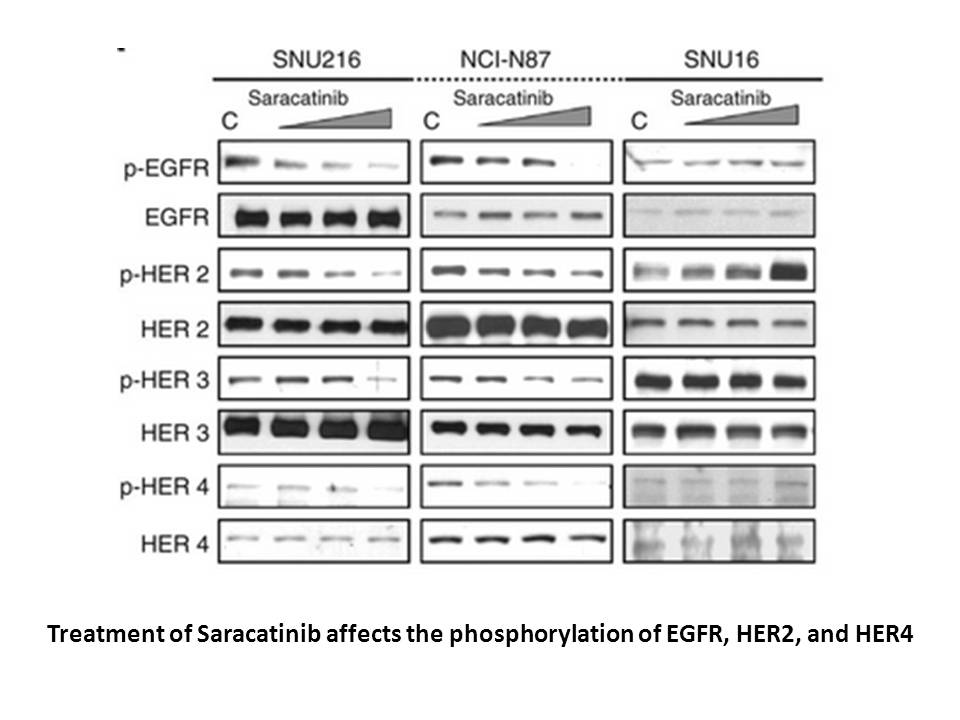
The Wnt signaling pathway has been demonstrated to be responsible for a variety of biological processes. The three best-characterized Wnt signaling pathways are the canonical Wnt pathway, the noncanonical planar cell polarity pathway, and the noncanonical Wnt/calcium pathway. The canonical Wnt/β-cat
-
br Introduction The identification of
2020-06-29
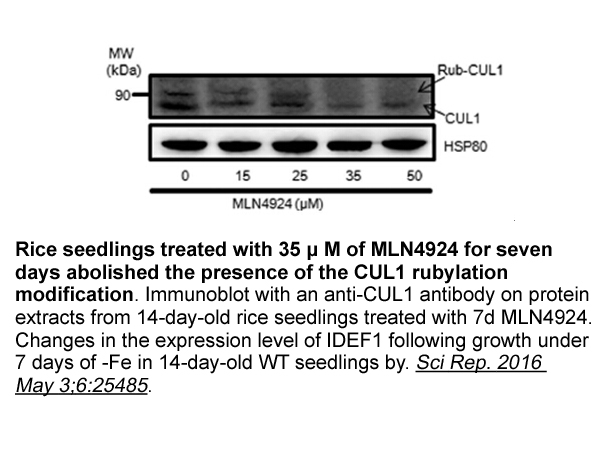
Introduction The identification of genetic variants that influence susceptibility to Parkinson\'s disease (PD) determines functional studies, the generation of model systems and directs therapeutic strategies. To date, classical candidate gene association studies and genome-wide approaches have f
-
sodium channels In Hevea brasiliensis both the soluble PPase
2020-06-28
In Hevea brasiliensis, both the soluble PPase and the membrane-bound V-PPase are present in the latex; the soluble PPase is in the C-serum (cytosol) of the latex [6] and the V-PPase is on the tonoplast of the lutoid, a special vacuole in the laticifers of rubber trees [7]. The V-PPase on the lutoid
-
Given the importance of cysteine cathepsin inhibitors as put
2020-06-28
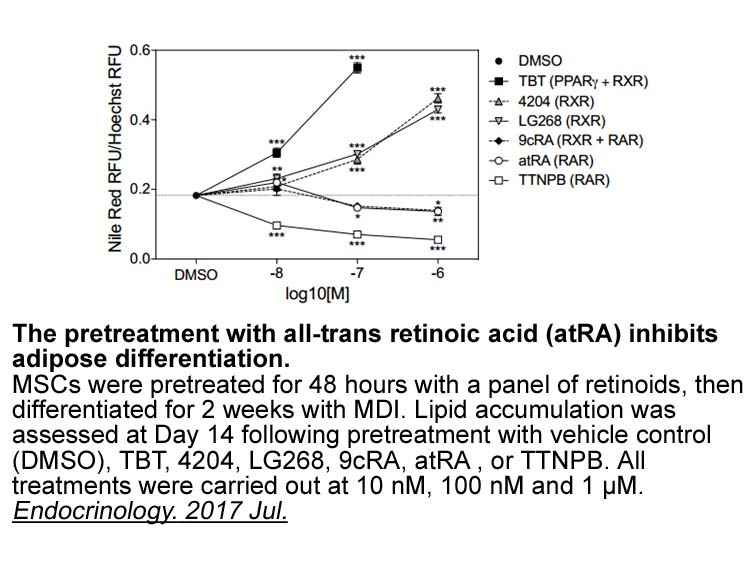
Given the importance of cysteine cathepsin inhibitors as putative therapeutic molecules and microbial virulence factors, we chose to investigate whether Yersinia enterocolitica may be a potent producer of such inhibitors. Y. enterocolitica is the most heterogeneous species within the genus Yersinia.
-
Zoledronic Acid Cells expressing the CDK S D
2020-06-28
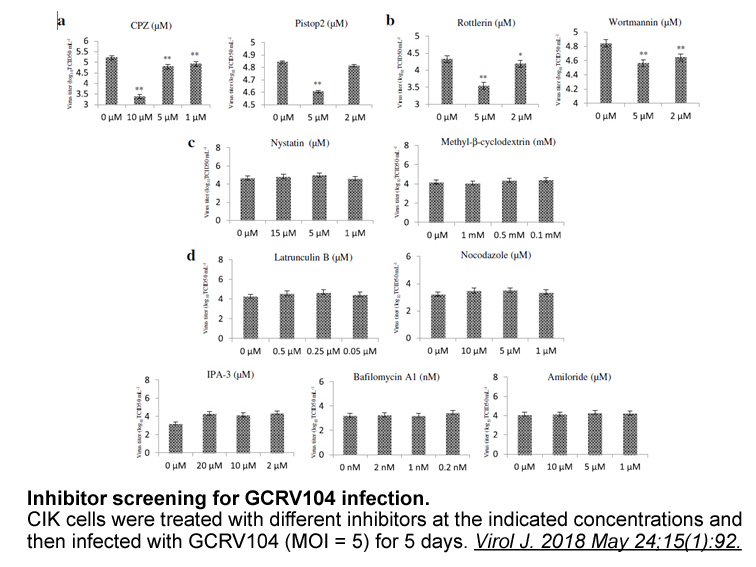
Cells expressing the CDK5 S47D mutant exhibit impaired migration and enhanced proliferation: Finally, we wished to determine the functional significance of this phosphoevent. Multiple studies have implicated active CDK5 in promotion of cell migration [9,16,[21], [22], [23], [24]] and in one study th
15416 records 795/1028 page Previous Next First page 上5页 791792793794795 下5页 Last page